
Faq - diabetic retinopathy
What is diabetic retinopathy?
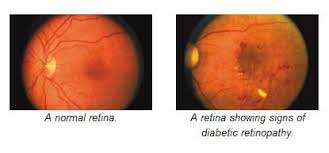
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common eye disease among people with diabetes mellitus – either type I or type II. High blood sugar can damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina. The weakened blood vessels may leak fluid and blood damaging the retina and causing loss of vision.
Who is at risk for developing diabetic retinopathy?
All diabetics both type I and type II are at risk for developing diabetic retinopathy. Patients can develop retinopathy either if they have very poorly controlled blood sugar levels and / or they have diabetes mellitus for a longer duration in their life. In addition, high blood pressure, high cholestrol, anemia, kidney disease, pregnancy can all place a patient at a greater risk for developing diabetic retinopathy.
How can diabetes affect the eyes?
- - High blood sugar can damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina.
- - The tiny blood vessels may swell and get clogged and do not allow enough blood to flow through
- - These tiny blood vessels swell and become leaky and fluid leaks from these damaged vessels into the retina
- - As diabetic retinopathy worsens, new blood vessels grow on the retina
- - These blood vessels are structurally very weak and break easily and therefore leak blood into the vitreous of the eye
- - The leaking blood keeps light from reaching the retina
- - In the laters stages, detachment of the retina occurs.
What are the symptoms of diabetic retinopathy?
In the early stages, there might not be any symptoms since the central portion of the retina may not be involved. As the retinopathy advances, the patient may notice
- - Blurred vision
- - Floaters which are tiny black spots, little threads or cobwebs floating in front of the eyes
- - Sudden loss of vision if there is bleeding inside the eye
- - Temporary or permanent loss of vision
What are the types of Diabetic Retinopathy?
Non – proliferative
This type of diabetic retinopathy refers to the early stage of the disease
Proliferative
This refers to the severe advanced stage of the disease when leaky, structurally weak, new blood vessels develop on the retina
Macular edema
This develops at any stage of the disease. Fluid and exudates collect in the macula of the retina (central part of the retina responsible for crisp, sharp and clear vision)
How to prevent diabetic retinopathy?
Although it may be totally possible to prevent development of diabetic retinopathy, keeping blood sugar under control along with good control of other parameters like blood pressure, cholestrol levels will help minimize the risk to a great extent.
How frequently should i get my eye examined?
If you have diabetes, you should get an annual eye examination done by your ophthalmologist. One you develop diabetic retinopathy, the ophthalmologist will advise further investigations and treatment. A periodic follow up, the frequency of which will be decided and advised by your ophthalmologist based on the severity of the disease is mandatory.
How is diabetic retinopathy treated?
There are different methods of treatment of diabetic retinopathy based on the presentation and severity of the disease. The various methods available are
- - Laser photocoagulation
- - Intravitreal injection
- - Vitrectomy
The treatment best for you will be decided by your ophthalmologist
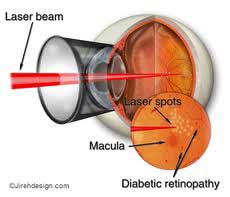
What is laser treatment and how successful is it?
The aim of laser treatment is not restore lost vision but to preserve existing vision. Laser beam delivered to the eye shrinks the abnormal blood vessels so that they no longer leak. This may lead to tiny spots in your field of vision which usually fade and disappear with time.
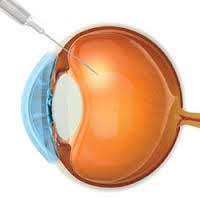
What are intravitreal injections and what is their role in management of diabetic retinopathy?
There are certain mediciations called Anti - VEGF (anti – vascular endothelial growth factors) like Lucentis, Avastin, Macugen which are injected into the eye as intravitreal injection in diabetic macular edema and proliferative diabetic retinopathy. They prevent development of new, leaky vessles on the retina. They are used along with laser treatment for treatment of diabetic vitreous hemorrage and retinal detachment.
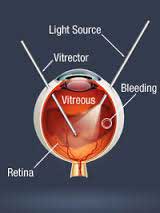
What is vitrectomy?
Vitrectomy is a surgical procedure where all the blood in the vitreous is removed and all abnomal adhesions excied. This is usually done when the patient presents in advanced stage with either hemorrhagein the vitreous or with retinal detachment.
Will I go blind if i suffer from Diabetic Retinopahthy?
YES, if the disease progresses and is not treated at an early stage, there is chance for visual loss.
What should I do if I have Diabetic Retinopathy?
- - Keep your blood glucose level and blood pressure under control
- - Have an annual eye examination by your ophthalmologist and call your eye doctor between scheduled examinations if you have any problems o r questions
- - Eat a healthy balanced diet, watch your weight, do mild exercise everyday
- - Quit smoking
